How to use E-volve
A fast tutorial for new users
How to use
E-Volve recieves as entries some protein complex in PDB format, a list of mutations and pairs of chains to be analyzed. These entries are detailed below.Input Data
Protein PDB
The first field is to upload the PDB file from your computer, while the second entry is for insert the PDB ID of the protein complex you want to mutate, and we will fetch the file from PDB.Mutation
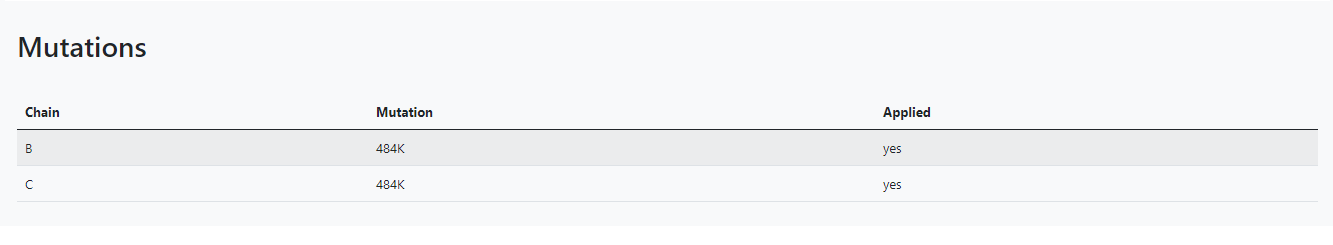
Here you can choose the mutations you want to apply to the protein complex, and you can either mutate or delete. You must follow the format Chain: Residue Position Residue Name. For example, E:484K, where the residue 484 from the E chain will be changed for a K(Lysine).Chain Pairs
In this field, you must select the chain pairs of some region of interest from the protein complex, for the contact calculation. You must write the name of the chain exactly as in the PDB file (capital letter and only one letter). If you want to select more chain pairs you have to click on the add pairs button.Output Info
Download
Shows the time it took to execute E-Volve contacts and allows the user to download the original and mutated PDB files. Also shows what was the modeling way used: Modeller standard fast model or Modeller mutate.py script.
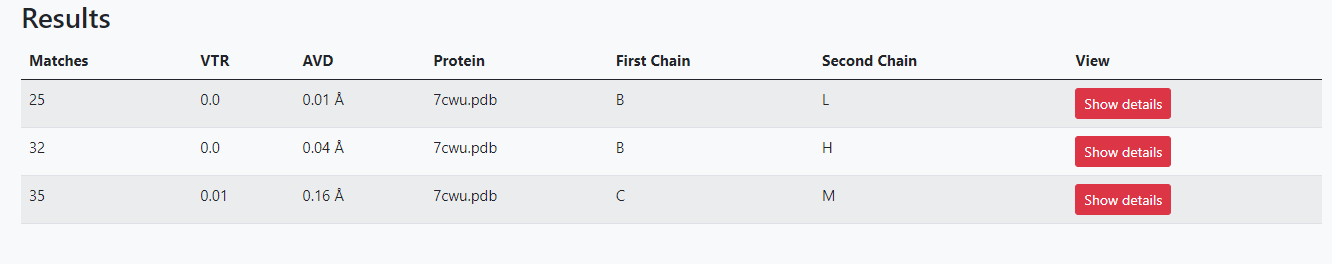
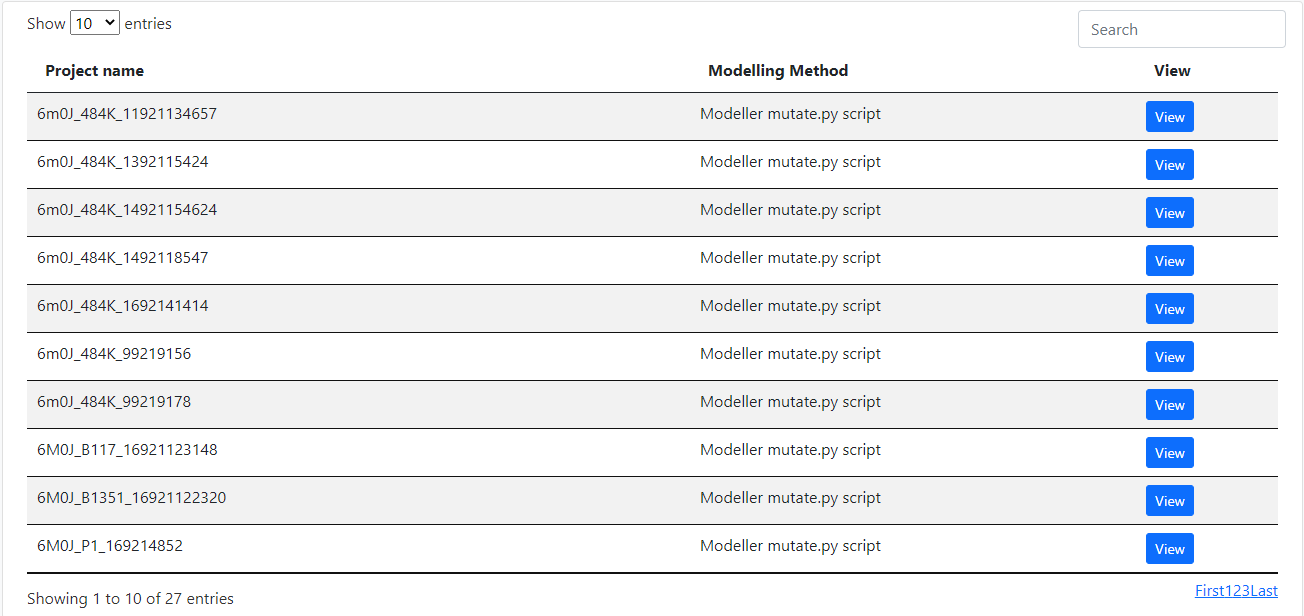
Analysis
A table that contains general information about the contact match. The user can click on the "View" button to access the contact analysis of each chain pair.
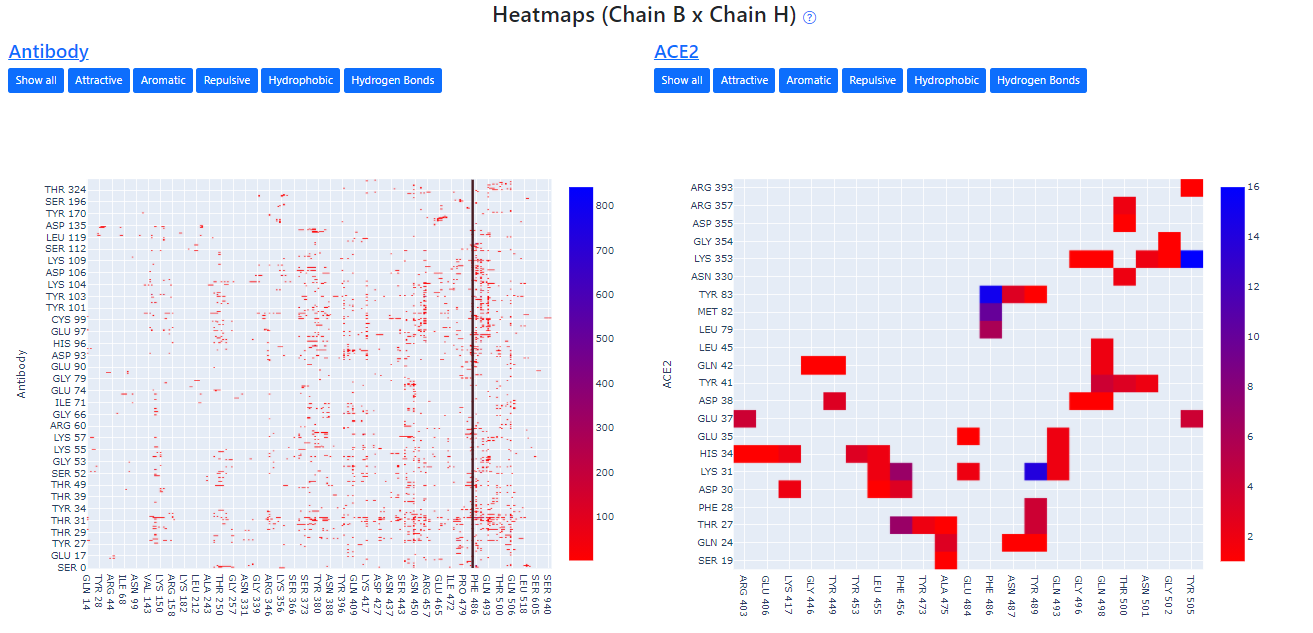
Heatmaps
The heatmaps are a superposition of all contact maps of spike-antibody and spike-ACE2 that we built in our Database, the gradient of colors varies from red to blue, representing a small number of contacts and a numerous number of contacts, respectively, between that pair of residues. E-Volve also highlights the mutations provided by the user, giving a notion of how the mutations can affect the protein interactions with antibodies or ACE2.